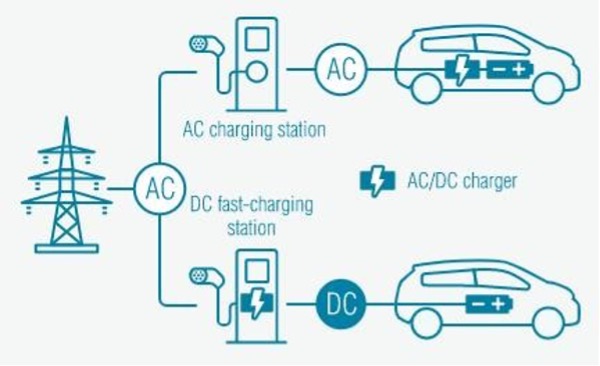
You could say that there are 2 different types of ‘fuels’ for charging your car. Namely AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current). On the electricity grid there is always AC. However, all batteries, including those of electric/hybrid cars, can only store DC. Most devices with a battery therefore have a built-in converter in the plug.
AC charging:
In the electric/hybrid vehicles there is already an integrated charger (converter). So AC comes in here and is converted to DC and then goes to the car battery. Currently, this is the most common charging method for electric vehicles. But beware! There are different converters, not every converter can convert the same amount of current. So this will have an effect on the charging speed of your vehicle.
DC charging:
The difference between DC and AC charging is the location where the AC power is converted to DC power. With DC charging, this already happens outside the car. Unlike AC chargers, DC chargers have the converter already inside the charger. This allows the power to go directly to the battery and does not need to be converted by the integrated charger. DC chargers are faster and larger but their complexity also makes them more expensive to manufacture and install.
How fast your car charges depends on the car (integrated charger) and the power of the charging point. The NRGkick can charge up to 22kW if your car allows it.
Translated with www.DeepL.com/Translator (free version)